SCCM vs. Intune: A Comprehensive Guide to Microsoft Device Management Tools

This comprehensive guide is expertly crafted by the professionals at Easy2Patch. Through this exploration, you can trust the expertise of Easy2Patch to provide insightful analyses and practical recommendations for navigating SCCM
and Intune.
Microsoft's device management tools, System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM), and Intune are stalwarts in IT administration. They offer organizations powerful solutions to streamline and enhance their IT environments. These tools offer diverse features to handle devices, applications, and data. SCCM, with its roots as a traditional endpoint management solution, thrives in environments anchored by on-premises servers and a workforce steeped in on-premises practices.
Contrastingly, Intune emerges as a cloud-based mobile device management (MDM) solution, excelling in highly homogeneous environments and proving invaluable for organizations navigating the complexities of a hybrid workforce. Its versatility spans device management for workstations, laptops, tablets, and mobile devices across diverse end-user operating systems.
Both SCCM and Intune bring to the table their distinctive strengths and limitations, necessitating a nuanced understanding to make an informed choice tailored to your organization's specific IT needs.
A Short Journey through the History of SCCM and Intune
Microsoft has played a significant role in shaping systems management through its key products: SCCM and Intune.
In 1994, Microsoft introduced the "Systems Management Server" (SMS), addressing needs such as remote control, patch management, software distribution, and hardware and software inventory. SMS laid the groundwork for what would later evolve into "ConfigMgr". Over time, SMS transformed into System Center Configuration Manager, a powerful systems management software crucial for organizations. It offers advanced features like operating system deployment, becoming a robust solution for efficiently managing large groups of computers.
Recognizing the broader functionality of Windows Intune beyond the Windows ecosystem, Microsoft rebranded it as Microsoft Intune in 2014. This shift aimed to position the service as a comprehensive cloud-based solution for managing a diverse range of devices, regardless of their operating systems.
A significant milestone occurred in 2019 with the introduction of Microsoft Endpoint Manager. This innovative solution seamlessly integrated ConfigMgr and Intune into a unified endpoint management platform. This convergence marked a paradigm shift, enabling organizations to centrally manage desktops, laptops, servers, and mobile devices from a single, consolidated console.
Today, Microsoft Endpoint Manager stands as a testament to Microsoft's commitment to providing organizations with a powerful and integrated approach to endpoint management. As we've traced the evolution of SCCM and Intune in our historical journey, let's now embark on a thorough exploration of SCCM in the upcoming section: 'SCCM: An In-depth Overview.'
SCCM: An In-depth Overview
Knowing SCCM's key aspects is vital for efficient IT management,
optimizing system performance, and addressing potential challenges.
Here's an in-depth look at its key features, advantages,
and limitations from Easy2Patch experts.
What are the key features of SCCM?
SCCM encompasses a range of powerful features that enhance the management of IT infrastructure. From deploying operating systems to scheduling updates and integrating with Microsoft Intune, it offers a suite of tools for administrators:
OS DeploymentSCCM facilitates the creation and deployment of operating system images, streamlining the process of provisioning and configuring devices.
Remote ControlAdministrators can take control of remote devices, enabling efficient troubleshooting and performance issue resolution without the need for physical access.
Maintenance WindowsUsers can define specific time windows for configuration management tasks, ensuring updates and maintenance activities do not disrupt productivity.
Integration with Microsoft IntuneSCCM seamlessly integrates with Microsoft Intune, extending management capabilities to mobile devices running iOS, Android, and Windows operating systems.
SchedulingThe scheduling feature allows administrators to plan and execute updates, ensuring the network infrastructure is regularly updated to minimize vulnerabilities.
ReportingSCCM empowers users to generate comprehensive reports on system status, patch levels, and more. For instance, users can create reports highlighting systems with missing patches.
Endpoint ProtectionCentralized management of anti-malware policies and firewall security provides a holistic approach to protecting computers across the network. Updates can be efficiently distributed to Windows 10 devices.
What are the advantages of using SCCM?
SCCM offers distinct advantages that streamline IT management processes and enhance overall organizational efficiency:
Simplified Deployment and ComplianceSCCM streamlines application deployment, patching, and compliance processes, reducing manual efforts and enhancing overall efficiency.
Comprehensive ReportingThe tool offers robust reporting features, enabling users to monitor project progress, track system status, and gather valuable insights for informed decision-making.
Automated Software InstallationsSCCM maintains regulatory compliance throughout the deployment process by automating software installations.
What are the limitations of SCCM?
Despite its strengths, SCCM does have some limitations that organizations should consider when evaluating its suitability for their specific needs.
Limited Support for Non-Windows DevicesSCCM's primary focus on Windows devices may pose challenges for organizations with diverse device ecosystems, as its support for non-Windows platforms is limited.
Extended Third-Party Patch Deployment with Additional Tools in SCCMWhile excelling in managing Microsoft updates, SCCM's support for third-party application patches is somewhat restricted, requiring additional considerations for comprehensive patch management.
Complex and Expensive PricingThe complexity and cost of SCCM licensing may present challenges for some organizations, necessitating careful evaluation of budget considerations and alternative solutions. As we wrap up our look at SCCM, let's shift gears to explore 'Intune: A Comprehensive Analysis,' delving into its features, pros, and cons.
Intune: A Comprehensive Analysis
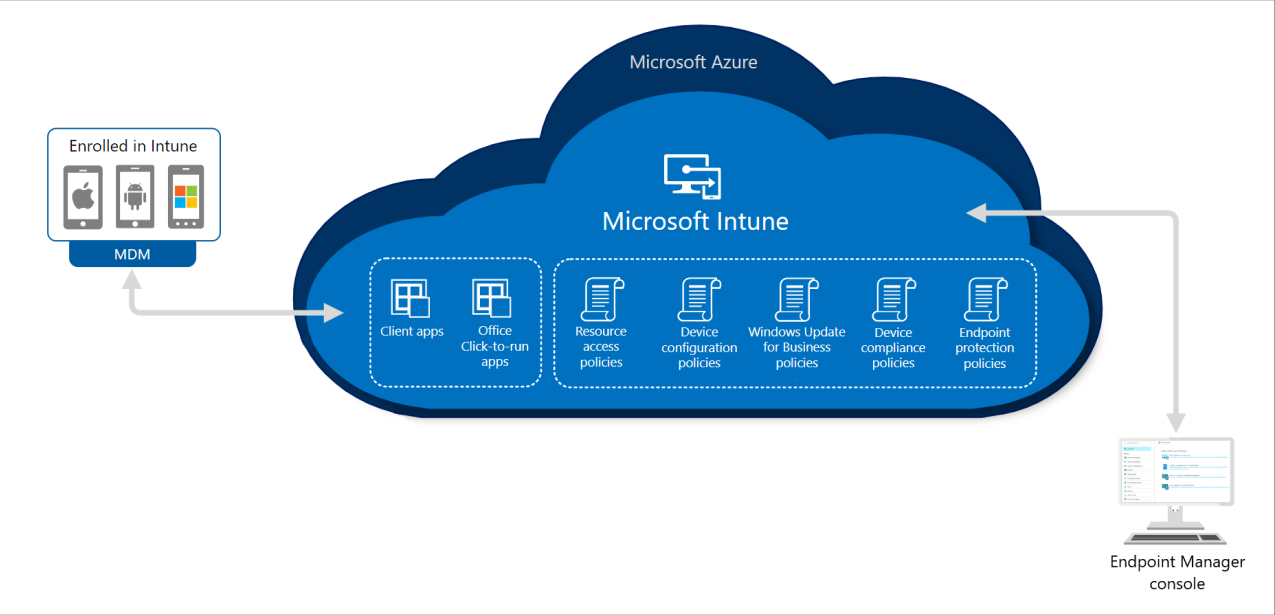
What are the key features of Intune?
From device management to application deployment, Microsoft Intune offers an array of features designed to streamline operations across various platforms.
Device ManagementIntune's device management capabilities are comprehensive, extending support to both organizational and personally owned devices. Its compatibility spans across Android, iOS, Linux, macOS, and Windows, ensuring a holistic approach to device administration.
Application ManagementSimplifying the complexities of application management, Intune provides a built-in app experience. Application management includes deployment, updates, and removal, offering flexibility in connecting and distributing apps from private stores, deploying Win32 apps, and creating app protection policies.
IntegrationBy excelling in integration, Intune fosters collaboration with other Microsoft services, applications, and third-party partners, ensuring a seamless experience for users across various platforms and ecosystems.
Automated Policy DeploymentAutomation lies at the core of Intune's functionality. It automates policy deployment for apps, security, device configuration, compliance, and conditional access, enhancing efficiency in managing diverse aspects of the digital infrastructure.
What are the pros of adopting Intune?
The adoption of Microsoft Intune comes with several advantages, making it a preferred choice for organizations seeking comprehensive mobile device and application management solutions.
Support for a Diverse Mobile EcosystemIntune's broad support for major operating systems makes it an ideal choice for organizations with diverse device environments, ensuring a unified approach to device management.
Cloud-Based Mobile Ecosystem ManagementAs a cloud-based service focusing on mobile device management (MDM) and mobile application management (MAM), Intune offers flexibility, accessibility, and seamless updates, enhancing overall management efficiency.
Data ProtectionIntune places a strong emphasis on data protection at the application level, providing a secure environment for managing sensitive information and mitigating potential security risks.
IntegrationThe seamless integration of Intune with Microsoft products and third-party systems enhances overall productivity, offering a cohesive experience within the organizational ecosystem.
FlexibilityIntune's flexibility allows it to grow alongside businesses, providing scalability and adaptability to changing requirements over time.
What are the cons of deploying Intune?
Despite its strengths, Intune is not without limitations. Understanding the drawbacks is crucial for organizations considering its deployment for their digital management needs.
Intune's VersatilityIntune's primary focus on mobile devices may limit its effectiveness for organizations requiring a more comprehensive systems-management platform. Intune extends its management capabilities beyond mobile devices, encompassing PCs and laptops as well. With the integration of Endpoint Manager, organizations can benefit from a more comprehensive systems-management platform.
Lack of Server SupportThe absence of support for server-side applications can be a drawback in environments where server management is a critical component of the overall infrastructure. Intune is not designed to manage server operating systems.
Planning ChallengesOrganizations may encounter difficulties in predicting and managing the frequency and size of software updates over time, impacting planning and resource allocation.
Limited Scalability and Custom Report CreationWhile Intune may not match SCCM in terms of extensive customization options, recent improvements have enhanced its scalability and reporting capabilities. Intune now offers a variety of reporting features, showcasing progress in areas like scalability and reporting. Organizations can leverage its evolving capabilities for effective device management. Having navigated through the depths of SCCM and Intune in our preceding sections, let's pivot to a technical comparison in our next section: 'SCCM vs. Intune.'
SCCM vs. Intune
The comparison between Microsoft's System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) and Intune is crucial for IT decision-makers as it helps navigate the complexities of diverse endpoint management needs. This insightful comparison, crafted by Easy2Patch experts, serves as a guide for IT professionals seeking optimal solutions to meet their diverse endpoint management needs.
Deployment and Management
Intune:Intune utilizes a profile-based approach to device management, following the guidelines prescribed by the operating system manufacturer. This approach simplifies the management of mobile devices, but it has certain limitations inherent to any Mobile Device Management (MDM) solution. Intune is confined to a specific set of prescribed APIs provided by Microsoft, limiting its capabilities in managing devices. The scalability of Intune is noteworthy, making it suitable for smaller to medium-sized businesses. It excels in environments that require finesse, such as managing updates for mobile devices and applications. It's worth noting that Intune's capabilities have expanded over time and it can manage PCs and laptops, not just mobile devices.
SCCM:In contrast, SCCM adopts an agent-based approach to endpoint management, installing agents on each endpoint. SCCM provides administrators with direct access to the devices. However, this approach is more complex, demanding significant management and setup efforts. It is particularly suitable for large organizations that require intricate endpoint management. SCCM is recognized for its scalability, making it an optimal choice for organizations with substantial device fleets and complex heterogeneous environments. It is well-suited for significant tasks like deploying Windows 10 on bare metal machines. It's important to note that SCCM can also manage some non-Windows platforms, although it's primarily Windows-centric.
Security Features
Intune:Intune is designed to manage a diverse range of devices, including those running iOS, Android, Windows, and macOS, contributing to its effectiveness in handling heterogeneous environments. This capability allows organizations with various device types to benefit from Intune's features. The platform excels in device, app, user, and password management, making it suitable for organizations with a diverse device landscape. The user experience with Intune is generally streamlined, emphasizing ease of use and straightforward interfaces.
SCCM:SCCM offers a broader range of security features, including Endpoint Protection, Compliance and Settings Management, and Client Health and Monitoring. This feature makes it a comprehensive solution for organizations dealing with complex and heterogeneous environments. The user experience for SCCM may have a steeper learning curve due to its extensive feature set, but it provides robust security capabilities for diverse endpoint environments. It's important to note that Intune also provides robust security capabilities, especially when integrated with other Microsoft security solutions.
Integration Capabilities
Intune:Intune integrates with other Microsoft products and supports a hybrid workforce, making it adaptable to diverse organizational needs. Its compatibility with various Microsoft technologies ensures a smooth integration process.
SCCM:SCCM integrates with various Microsoft technologies, such as Application Virtualization (App-V), Enterprise Desktop Virtualization (Med-V), Citrix XenApp, Microsoft Forefront, and Windows Phone applications. This extensive integration capability enhances its versatility in managing diverse environments. SCCM's automation and scripting capabilities are particularly beneficial for organizations relying heavily on these functionalities. Both Intune and SCCM offer strong integration with Microsoft products. Intune's integration is cloud-centric, while SCCM's integration extends to on-premises solutions.
Cost Efficiency
Intune:Intune operates on a monthly subscription model, and the cost can be scalable, making it potentially cost-effective for organizations with fluctuating device counts. The flexibility of its subscription model caters well to organizations with varying device counts and budget structures.
SCCM:SCCM's cost structure extends beyond upfront implementation costs, encompassing potential expenses for maintenance, infrastructure, and additional CALs (Client Access Licenses). While there are no monthly subscription charges, this comprehensive approach to costs ensures a nuanced understanding of the financial implications. This feature can lead to a more cost-effective solution, especially beneficial for larger organizations managing extensive device fleets. SCCM's cost structure aligns seamlessly with the preferences of organizations looking for a one-time investment model and long-term cost predictability.
Scalability
Intune:Intune is not limited to smaller to medium-sized businesses; it is designed to seamlessly scale to meet the demands of large enterprises, particularly when integrated with other Microsoft cloud services. Its cloud-based architecture ensures unparalleled flexibility and adaptability, making it an ideal solution for organizations of varying sizes and evolving business requirements.
SCCM:SCCM is recognized for its scalability, making it an optimal choice for large enterprises with substantial device fleets and complex heterogeneous environments. Its on-premises architecture accommodates the requirements of organizations managing extensive and diverse IT infrastructures.
User Experience
Intune:Intune offers a streamlined user experience with an emphasis on ease of use and straightforward interfaces. It is designed to be user-friendly, making it accessible to administrators and end-users alike.
SCCM:The user experience with SCCM may have a steeper learning curve due to its extensive feature set. However, this complexity is justified by the comprehensive control it provides over diverse endpoints. SCCM is suitable for organizations where administrators are well-versed in managing intricate IT environments.
Device Types
Intune:Intune, as a cloud-based Mobile Device Management solution, is designed for managing devices in homogeneous environments. It effectively handles workstations, laptops, tablets, and mobile devices.
SCCM:SCCM is tailored for the management of complex and heterogeneous environments, including servers, laptops, and workstations. It is suitable for organizations with diverse device types and operating systems.
Deployment Flexibility
Intune:Intune offers flexibility in deployment options, supporting cloud-based, on-premises, and hybrid deployment scenarios. This adaptability caters to the varied needs of organizations with different infrastructure preferences.
SCCM:SCCM offers deployment flexibility through on-premises architecture, making it ideal for organizations with a traditional on-premises workforce and infrastructure. It may also be deployed in a hybrid scenario, combining on-premises and cloud-based elements.
Automation and Scripting
Intune:Intune provides support for automation and scripting, enabling streamlined configuration and management tasks. This feature proves advantageous for organizations leveraging scripted processes in device management.
SCCM:SCCM is renowned for its extensive automation and scripting capabilities, positioning itself as a formidable tool for organizations with advanced scripting requirements. It offers meticulous control over configuration tasks and sophisticated automation processes, setting it apart in the realm of advanced management solutions.
Update Management
Intune:Intune efficiently manages updates for mobile devices and applications, ensuring that devices are up-to-date with the latest patches and features.
SCCM:SCCM excels in software update management, offering extensive control over update deployment for a diverse range of devices and applications, encompassing servers, workstations, and other endpoints.
Community Support and Documentation
Intune:Intune benefits from a supportive community and comprehensive documentation, offering resources for administrators and users to troubleshoot issues and access helpful information.
SCCM:SCCM has a well-established community and extensive official documentation, providing valuable resources for administrators dealing with the complexities of endpoint management in large-scale environments.
Compliance and Reporting
 Intune:
Intune:
Intune provides essential features for compliance and reporting, ensuring that organizations can meet regulatory requirements and maintain visibility into their device landscape.
SCCM:SCCM offers robust capabilities for compliance and reporting, enabling organizations to enforce policies, monitor device health, and generate detailed reports for auditing and analysis purposes.
Deciding between Intune and SCCM depends on the specific needs of the organization. Intune is well-suited for smaller to medium-sized businesses with a focus on mobile device management, while SCCM excels in large enterprises managing complex and diverse IT environments. The choice should align with the organization's size, infrastructure, and the level of control required over endpoint management.
Below is a comparison table summarizing the key points discussed for SCCM (System Center Configuration Manager) and Intune:
| Aspect | Intune | SCCM |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment and Management | Profile-based approach for device management. | Agent-based approach with installation on each endpoint. |
| Security Features | Focus on device, app, user, and password management in homogeneous environments. | Broader range of security features, including Endpoint Protection, Compliance, and Settings Management. |
| Integration Capabilities | Seamless integration with other Microsoft products, supports a hybrid workforce. | Integrates with various Microsoft technologies, providing versatility in managing diverse environments. |
| Cost Efficiency | Monthly subscription model, potential accumulation of costs for a large number of devices. | Upfront implementation costs, no monthly subscription charges, cost-effective for larger organizations. |
| Key Features | Remote device management, app management, user management, and password management. | Comprehensive set of features, covering Windows 10 Management, Application Delivery, Compliance, and more. |
| Scalability | Well-suited for smaller to medium-sized businesses. | Recognized for scalability, optimal for large enterprises managing complex and heterogeneous environments. |
| User Experience | Streamlined user experience with an emphasis on ease of use. | May have a steeper learning curve due to its extensive feature set, suitable for administrators with experience. |
| Device Types | Designed for managing devices in homogeneous environments, including workstations, laptops, tablets, and mobile devices. | Tailored for managing complex and heterogeneous environments, including servers, laptops, and workstations |
| Deployment Flexibility | Offers flexibility in deployment options, supporting cloud-based, on-premises, and hybrid scenarios | Provides flexibility in deployment with on-premises architecture, suitable for traditional on-premises workforce. |
| Automation and Scripting | Supports automation and scripting capabilities for efficient configuration and management tasks | Known for robust automation and scripting capabilities, providing granular control over configuration tasks. |
| Update Management | Efficiently manages updates for mobile devices and applications. | Excels in software update management, providing comprehensive control over updates for various devices and applications. |
| Community Support and Documentation | Benefits from a supportive community and comprehensive documentation. | Has a well-established community and extensive official documentation, offering valuable resources. |
| Compliance and Reporting | Provides essential features for compliance and reporting. | Offers robust capabilities for compliance and reporting, enabling organizations to enforce policies and monitor device health. |
The Future of Device Management: SCCM and Intune

SCCM, once considered a staple, is now labeled as a 'legacy' product, sparking speculation about its future. SCCM is indeed transitioning from its traditional on-premises role. SCCM has evolved to support modern management tasks, including those needed for remote work scenarios. The co-management capability of SCCM allows it to work in tandem with Intune, providing a bridge to modern management while still supporting on-premises infrastructure.
Microsoft's transition to Intune has been a strategic move to overcome the challenges posed by SCCM. The abandonment of the cumbersome task of building and maintaining images using SCCM has been a pivotal change. The time-consuming process of downloading large files of 30GB or more every month is now a thing of the past. The evolution of Intune, initially lacking some of SCCM's functionalities, has been notable, with significant enhancements implemented in late 2020. Intune now boasts a cloud-based management infrastructure, leveraging the capabilities of the Microsoft Azure platform.
Microsoft continues to invest in co-management as a transitional strategy for organizations moving from SCCM to Intune. While the ultimate goal may be to shift entirely to cloud-based management with Intune, co-management remains a viable and important strategy for many organizations. As organizations prioritize efficient patch management, Easy2Patch offers a streamlined, user-friendly approach, ensuring devices remain consistently updated and secure.
How does Easy2Patch assist you with third-party patch management via SCCM or Intune?
Easy2Patch is a powerful software solution designed to streamline and centralize updating third-party products across computer networks within IT infrastructures. Seamlessly integrated with WSUS, SCCM, and Intune, Easy2Patch focuses on enhancing third-party patch management specifically for Windows Operating System Platforms.
Are you ready to revolutionize your third-party patch management? Easy2Patch is here to make that a reality! So, how can Easy2Patch assist you with third-party patch management via SCCM or Intune?
- Extensive Catalog: Easy2Patch boasts a comprehensive catalog comprising over 400 third-party applications and software options. This catalog is regularly updated with the latest patches, ensuring your software ecosystem remains robust and secure.
- Automated Patch Management: One of Easy2Patch's standout features is its ability to automate the patch management process. Automating updates maintains your software's consistency, minimizing the risk of vulnerabilities linked to outdated applications.
- Intune Integration: Easy2Patch seamlessly integrates with Microsoft Intune, utilizing the Intune Application Management feature. This integration facilitates the creation and deployment of third-party applications in Intune, providing system administrators with a user-friendly interface for efficient management.
- SCCM Integration: Easy2Patch seamlessly integrates with Microsoft SCCM for organizations, automating software updates, including third-party applications. This integration ensures centralized and well-managed control over update and installation processes.
- Defender Feature: Easy2Patch enhances security through its Defender feature, which automatically sends third-party applications to computers within predefined groups. System administrators can determine these groups based on the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) score, ensuring a targeted and proactive approach to patching vulnerable software.
- Premium Trial: Easy2Patch offers a 30-day premium trial, allowing users to experience all the features and advantages of the product firsthand. This trial period enables organizations to assess the effectiveness of Easy2Patch in improving their third-party patch management processes before committing to a full subscription.
Get started with our patch management software for free
Get 30 Day Premium TrialMaking the Right Choice for Your Business
Choosing between SCCM and Microsoft Intune depends on your business's specific needs. If you have a large on-premises infrastructure with diverse devices and need comprehensive control over software distribution and updates, SCCM is the optimal choice. It excels in managing traditional desktops, laptops, and servers within a centralized environment. On the other hand, if your business prioritizes cloud-based and mobile device management, especially with a remote or mobile workforce, Microsoft Intune is the ideal solution. It provides flexibility and easy management for modern devices with a user-friendly interface accessible from anywhere with an internet connection. The decision may also be influenced by reliance on third-party applications, where integration capabilities of both SCCM and Intune, along with tools like Easy2patch, enhance overall security and efficiency.
When should you use SCCM?
Consider using SCCM (System Center Configuration Manager) for comprehensive and centralized IT infrastructure management, especially in large enterprises with complex networks and diverse device environments. SCCM excels in handling traditional desktops, laptops, and Windows servers. It is an ideal choice for extensive control over software distribution, updates, and configuration settings. If an organization heavily relies on on-premises infrastructure and requires robust capabilities for managing software updates, including third-party applications like Easy2patch, SCCM's integration capabilities make it a powerful and efficient solution.
When should you use Microsoft Intune?
Microsoft Intune is the preferred cloud-based and mobile device management solution for businesses prioritizing these capabilities. It is particularly advantageous for organizations with a significant number of remote or mobile users, enabling device management from any location with an internet connection. Intune excels in handling modern devices, such as smartphones and tablets, extending beyond traditional desktops. It features a user-friendly interface for efficiently managing applications, updates, and security policies, making it suitable for organizations embracing a mobile and decentralized workforce. Intune, when paired with Easy2patch, seamlessly integrates for creating, deploying, and managing third-party applications, ensuring a streamlined and secure patch management process across diverse endpoints
Frequently Asked Questions
IT Automation Key Benefits and Best Practices

What Is Vulnerability Management?

Ultimate IT Risk Management Guide 2024: Best Practices, Strategies, and Tools

Best Practices for IT Infrastructure Management in 2024

What is Windows Patch Management? Features, Challenges, and Best Practices in 2024

What are the Cybersecurity Risks Associated with Outdated Software and Operating Systems?





